Call variants
Call variants.
Sofwtare
Software used in this practical:
- SAMTools : SAM Tools provide various utilities for manipulating alignments in the SAM format, including sorting, merging, indexing and generating alignments in a per-position format.
- Picard : Picard comprises Java-based command-line utilities that manipulate SAM files, and a Java API (SAM-JDK) for creating new programs that read and write SAM files.
- GATK : Genome Analysis Toolkit - A package to analyse next-generation re-sequencing data, primary focused on variant discovery and genotyping.
File formats explored:
- SAM
- BAM
- VCF Variant Call Format: see 1000 Genomes and Wikipedia specifications.
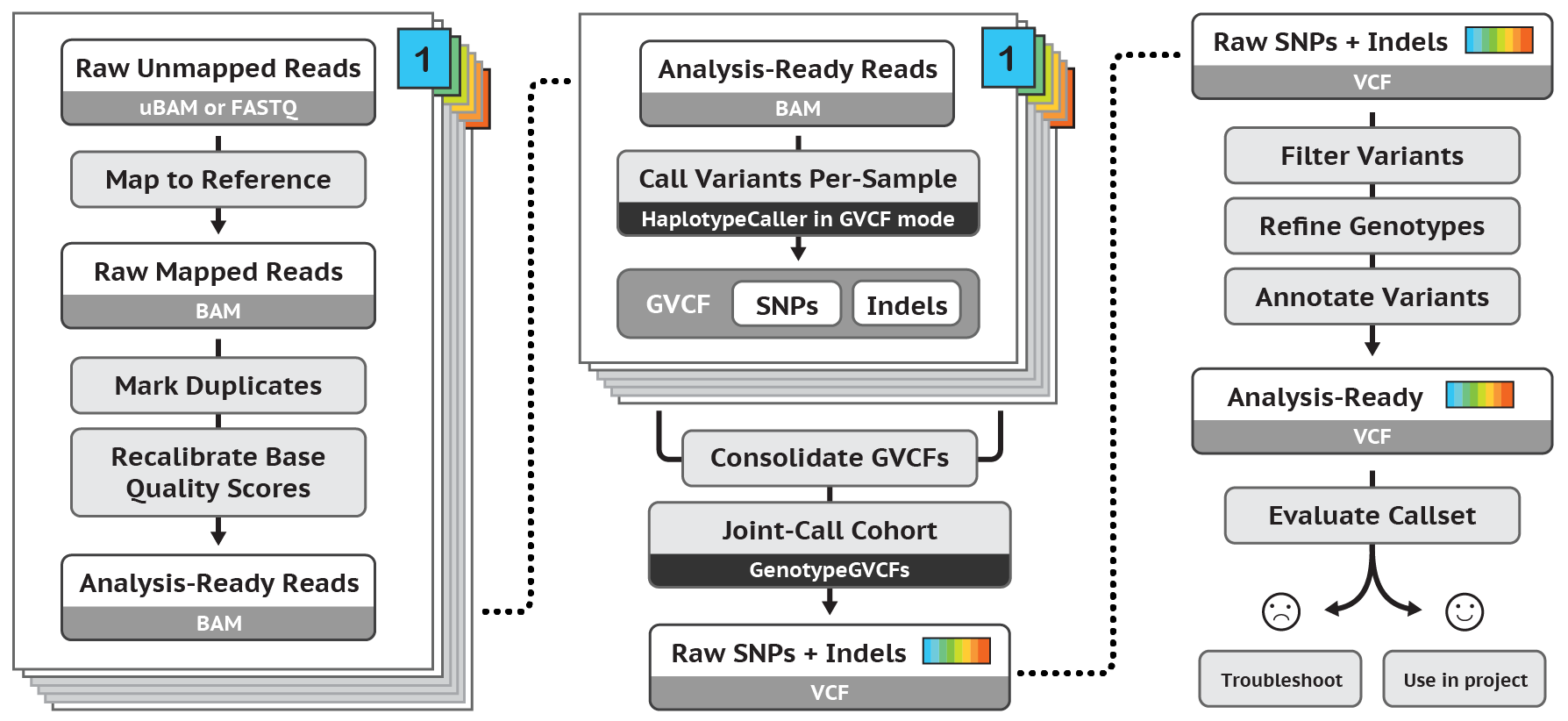
Exercise 2: Variant calling with pair-end data
Go to the example 1 folder in your course directory:
cd ~/Desktop/Data/CALL_VARIANT/
Prepare BAM file
We must sort the BAM file using samtools:
samtools sort example1/000-dna_chr21_100_hq_se.bam -o example1/001-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted.bam
Index the BAM file:
samtools index example1/001-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted.bam
Mark duplicates (using Picard)
Mark and remove duplicates:
picard MarkDuplicates \
INPUT=example1/001-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted.bam \
OUTPUT=example1/001-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted_noDup.bam \
METRICS_FILE=002-metrics.txt
Index the new BAM file:
picard BuildBamIndex INPUT=example1/001-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted_noDup.bam
Local realignment around INDELS (using GATK)
There are 2 steps to the realignment process:
Create a target list of intervals which need to be realigned
java -jar /home/bioinfo2/Data/Soft/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar \
-T RealignerTargetCreator \
-R genome/f000_chr21_ref_genome_sequence.fa \
-Iexample1/001-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted_noDup.bam\
-o 003-indelRealigner.intervals
Perform realignment of the target intervals:
java -jar /home/bioinfo2/Data/Soft/GATK/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar \
-T IndelRealigner \
-R genome/f000_chr21_ref_genome_sequence.fa \
-I example1/001-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted_noDup.bam \
-targetIntervals 003-indelRealigner.intervals \
-o 003-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted_noDup_realigned.bam
Base quality score recalibration (using GATK)
Two steps:
Analyse patterns of covariation in the sequence dataset
java -jar /home/bioinfo2/Data/Soft/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar \
-T BaseRecalibrator \
-R genome/f000_chr21_ref_genome_sequence.fa \
-I 003-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted_noDup_realigned.bam \
-knownSites 000-dbSNP_chr21.vcf \
-o 004-recalibration_data.table
Apply the recalibration to your sequence data
java -jar /home/bioinfo2/Data/Soft/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar \
-T PrintReads \
-R genome/f000_chr21_ref_genome_sequence.fa \
-I 003-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted_noDup_realigned.bam \
-BQSR 004-recalibration_data.table \
-o 004-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted_noDup_realigned_recalibrated.bam
Variant calling (using GATK - HaplotypeCaller)
java -jar /home/bioinfo2/Data/Soft/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar \
-T HaplotypeCaller \
-R genome/f000_chr21_ref_genome_sequence.fa \
-I 004-dna_chr21_100_hq_se_sorted_noDup_realigned_recalibrated.bam \
-o 005-dna_chr21_100_he_se.vcf
Once we have called the variants, we might be interested in filtering out some according to our confidence in them. Some of the most basic filters consist of identifying variants with low calling quality or a low number of reads supporting the variant. There are many programs that can be used to filter VCFs. Here we are going to use bcftools from Samtools to preform a basic filtering.
bcftools filter -s LowQual -e 'QUAL<20 | DP<3' 005-dna_chr21_100_he_se.vcf > 005-dna_chr21_100_he_se_filtered.vcf
Let’s see how many variants fail to pass our filters:
grep LowQual 005-dna_chr21_100_he_se_filtered.vcf | wc -l
And how many passed:
grep PASS 005-dna_chr21_100_he_se_filtered.vcf| wc -l
SOMATIC CALL
cd somatic_calling
samtools sort 000-normal.bam -o 001-normal_sorted.bam
samtools sort 000-tumor.bam -o 001-tumor_sorted.bam
samtools index 001-normal_sorted.bam
samtools index 001-tumor_sorted.bam
java -jar ~/soft/GATK/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar \
--analysis_type MuTect \
--reference_sequence TP53.hg19.fa \
--dbsnp 000-dbsnp_132_b37.leftAligned.vcf.gz \
--cosmic 000-b37_cosmic_v54_120711.vcf.gz \
--input_file:normal 001-normal_sorted.bam \
--input_file:tumor 001-tumor_sorted.bam \
--out 002-call_stats.out \
--coverage_file 002-coverage.wig \
--vcf 003-somatic_variants.vcf